Exploring Fasting's Impact on Long-Term Memory and Neurogenesis
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding Memory
Memory plays a crucial role in our lives, influencing how we learn and adapt. Unlike mechanical memories, human memories are abstract and intangible, existing as patterns of neuronal activity within the brain's intricate neural networks.
Memory is not a physical entity; it's an abstract construct shaped by various factors such as attention, perception, and emotion. Personal experiences and cognitive biases also affect how we remember and interpret past events.
The consensus among scientists is that memories are distributed across neural networks throughout the brain. When we encode or recall memories, specific neuronal activation patterns are triggered, allowing us to reconstruct stored information.
Memories serve as cognitive representations of our past experiences, knowledge, and skills, forming the foundation of our interactions with the world. They undergo three key processes: encoding, storage, and retrieval.
Section 1.1: Short-Term vs. Long-Term Memory
Short-term memory, often termed working memory, temporarily holds and manipulates information essential for cognitive tasks like reasoning and problem-solving. It has a limited capacity and duration, lasting just a few seconds to several minutes.
In contrast, long-term memory is a more enduring storage system, retaining information for extended periods, from minutes to a lifetime. It is vital for cognitive functioning, self-understanding, and emotional well-being.
Long-term memory shapes our identity and experiences, influencing our decisions and interactions. Understanding how long-term memories form and how to enhance them has significant implications across various fields.
Subsection 1.1.1: The Role of Long-Term Memory
Long-term memory enables us to learn from past experiences, adapt our behavior, and maintain our identities. It informs our actions and helps us communicate effectively. This type of memory also aids in emotional regulation, allowing us to cope with stress and maintain mental resilience.
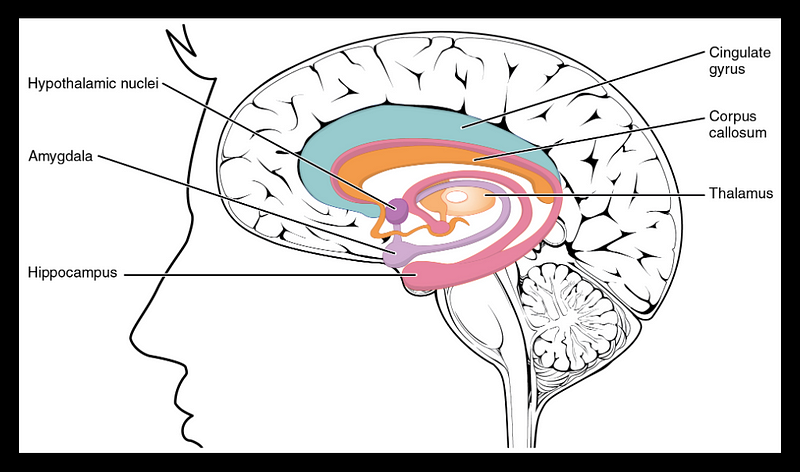
Chapter 2: The Science Behind Fasting and Memory
Recent studies reveal that fasting may enhance long-term memory and support neurogenesis in the hippocampus. Groundbreaking research published in 2013 in Science focused on the effects of fasting on memory formation in fruit flies.
According to the study, the formation of aversive and appetitive memories relies on different cellular activities, with fasting enhancing both types of memory formation. This suggests that fasting has a significant influence on how memories are encoded and retained.
In another notable 2021 study published in Nature, researchers found that intermittent fasting improved memory retention in mice, promoting neurogenesis and the expression of the longevity gene Klotho. The study concluded that intermittent fasting is more effective than simple caloric restriction in enhancing cognitive function.
The findings highlight the potential of fasting as a tool for improving cognitive health, suggesting that it enhances the brain's ability to generate new neurons, which is vital for memory consolidation and overall brain health.
Section 2.1: Hippocampal Neurogenesis Explained
Hippocampal neurogenesis is the process of generating new neurons in the hippocampus, a region essential for memory and learning. This dynamic process begins with neural stem cells, which differentiate into neuroblasts that mature into functional neurons.
Research indicates that neurogenesis plays a significant role in mood regulation and emotional processing, with implications for conditions like depression and anxiety. The ability to generate new neurons is linked to cognitive flexibility and adapting to new experiences.
In conclusion, fasting, combined with a healthy lifestyle, may provide substantial benefits for enhancing long-term memory and promoting neurogenesis. While fasting has proven effective for many, it is essential to approach it mindfully, considering individual health needs and potential risks.