The Impending Gulf Stream Collapse: Implications for 2025
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding the Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, scientifically referred to as the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), plays a crucial role in regulating the climate across the northern hemisphere. Recent research indicates that its collapse might be imminent, with projections suggesting it could occur as early as 2025. This development could usher in considerable global changes.
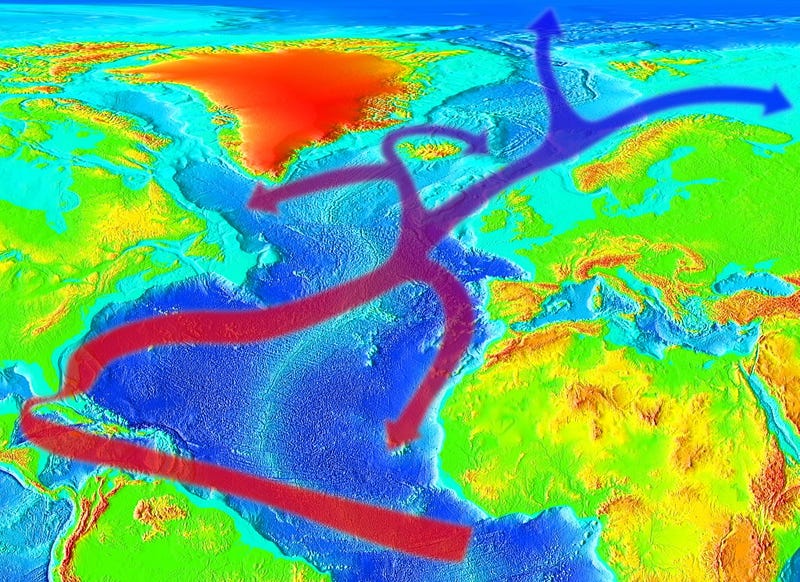
[Photo: RedAndr, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons]
The intricate oceanic current system is vital for transporting warm water from tropical regions to the northern Atlantic, thereby influencing climate. Current studies warn that if fossil fuel-related CO2 emissions persist at their current pace, the Gulf Stream could face a dramatic collapse by 2025. Such an event could lead to a rapid decrease in temperatures, upheaval of oceanic ecosystems, and an increase in storm activity globally.
Researchers from the University of Copenhagen assert there is a 95% probability that this ocean current system will collapse sometime between 2025 and 2095. Their most probable scenario points to around 2057 for this event. If this were to happen, certain regions in Western Europe could experience significant cooling. However, it is essential to note that this cooling would not put an end to the ongoing climate changes; global warming would continue to escalate, particularly in tropical areas.
Will there be a climate collapse in 2025?
To examine the Gulf Stream's status, the research team assessed sea surface temperatures in a particular segment of the northern Atlantic spanning from 1870 to the present. By employing advanced statistical methods, they aimed to yield more accurate predictions compared to earlier investigations.
The possibility of such an early prediction “astounded” researchers, as stated by Prof. Susanne Ditlevsen from the University of Copenhagen's Department of Mathematical Sciences. Their findings underscore the pressing need to comprehend and address how climate change impacts ocean currents and the potential ramifications for global climate dynamics.
Preventing the alarming scenario related to the Gulf Stream's potential collapse necessitates swift action to curtail greenhouse gas emissions, particularly those linked to fossil fuels. Climatologists have long urged immediate reductions in fossil fuel consumption to lessen climate impacts.
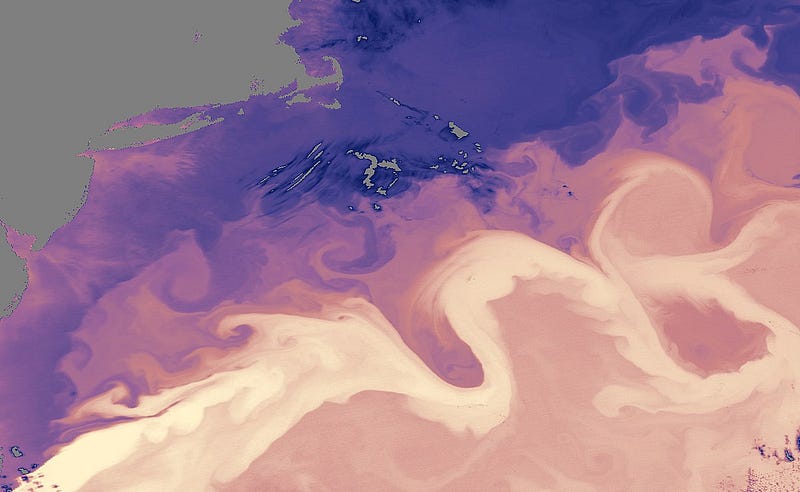
Transport of warm water revealed by the sea surface temperature distribution around the Gulf Stream — [Photo: NASA (data collected by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Aqua satellite), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons]
Regrettably, global initiatives aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions are sluggish and inadequate. Although significant actions are necessary, many nations continue to depend on fossil fuels, complicating the implementation of rapid changes.
Research on the Gulf Stream's potential collapse, while contentious, highlights critical issues regarding the future of our climate. Numerous scientists caution that the mathematical models underpinning these forecasts may be overly simplistic and rely on assumptions that require further scrutiny.
To truly grasp the risk of collapse and its climate impacts, ongoing research and monitoring of the Gulf Stream are essential. Nevertheless, assessments from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change indicate a full collapse of the Gulf Stream is unlikely within the 21st century. However, scientists persist in emphasizing the urgency of emission reduction efforts to avert severe consequences of climate change on a global scale.
Chapter 2: The Gulf Stream and Future Climate Dynamics
This video titled "Scientists warn Gulf Stream could collapse as early as 2025" details the urgent implications of the Gulf Stream's potential collapse and discusses the scientific findings that lead to these conclusions.
The second video, "Gulf Stream Collapse Could Cause Major Climate Shift," explores the broader climate implications of a potential Gulf Stream failure, providing insight into how global weather patterns may be affected.
Archaeological Discoveries: A Glimpse into the Past
Archaeologists have uncovered a Roman treasure from a shipwreck that dates back 2,000 years, located at a depth of 350 meters...
Thank you for reading! If you found this content valuable, please consider supporting my work through a donation or tip. Your generosity enables me to continue producing insightful content.

