The Legacy of Oppenheimer: How One Man Shaped Atomic History
Written on
Chapter 1: Oppenheimer's Early Years
- Robert Oppenheimer was a polarizing figure whose influence on the world is undeniable. Renowned for his contributions to theoretical and quantum physics, he was also instrumental in the advancement of nuclear reactors. Most notably, he is recognized as the father of the atomic bomb. This exploration delves into the life of one of humanity's most significant figures and the quest for atomic weapons, revealing a captivating narrative of science, ambition, and power.
The Beginning
Born in August 1904 in New York to Jewish parents, Oppenheimer's upbringing shielded him from the severe antisemitism prevalent in Europe. His early exposure to literature, music, and philosophy ignited his passion for science. He enjoyed a privileged education, attending prestigious private schools before enrolling at Harvard University in 1922. It was during his time at Harvard that he cultivated a strong interest in physics, graduating with a bachelor's degree after three years.
Following his graduation, Oppenheimer continued his studies at Christ's College, Cambridge University. Here, he collaborated with Nobel laureate Ernest Rutherford to investigate atomic structures, a pivotal experience for his future work on the atomic bomb. However, his time at Cambridge was not without struggle; he confided to a friend about his dissatisfaction with lab work, feeling unproductive and unfulfilled. Consequently, in 1926, he transferred to the University of Göttingen, a leading institution for theoretical physics, where he forged lasting friendships with notable scientists such as Werner Heisenberg, Enrico Fermi, Paul Dirac, and Pascual Jordan, ultimately earning his Doctor of Philosophy degree in 1927.
The Manhattan Project
After completing his PhD, Oppenheimer dedicated the next decade to teaching at various universities in the US and Europe, including Caltech and UC Berkeley. During this period, he authored numerous papers on nuclear physics and developed a growing interest in nuclear reactors. In October 1941, just two months before the United States entered World War II, Oppenheimer's life took a pivotal turn. President Roosevelt sanctioned a covert initiative known as 'The Manhattan Project' aimed at developing the first atomic bomb.
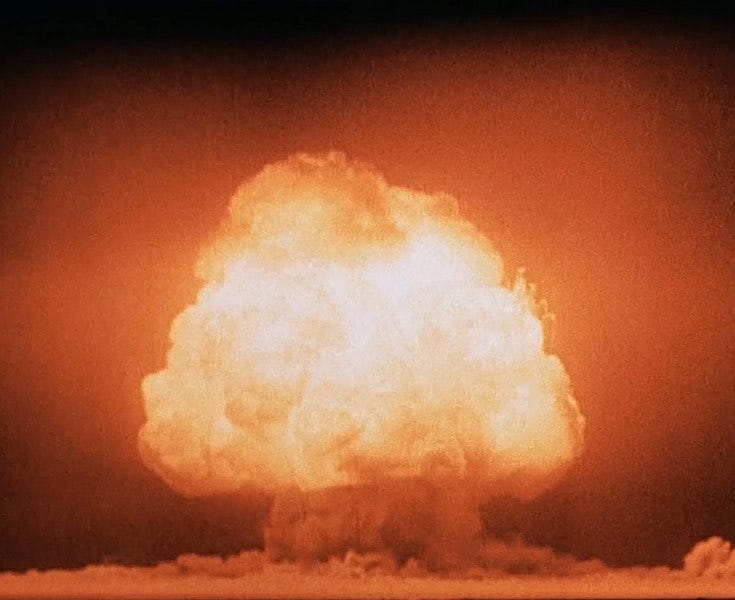
This top-secret project enlisted some of the era's most brilliant minds, and Oppenheimer was appointed to oversee its coordination. He gathered a team of scientists at Los Alamos National Laboratory in New Mexico, where they drew upon nuclear reactor technology to innovate a method for bomb creation. They discovered that bombarding unstable Uranium-235 atoms with neutrons led to their fission, releasing energy and additional neutrons, thus instigating a chain reaction.
With a workforce of 600 scientists and an investment of $2 billion, Oppenheimer's team successfully created an atomic bomb, with the first test scheduled just before President Truman's meeting with Stalin for peace negotiations. On July 16, 1945, the first atomic bomb was detonated at the Trinity Site in Alamogordo, New Mexico, resulting in an explosion equivalent to 25 kilotons of TNT. Shortly thereafter, two additional bombs were dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, effectively ending the war.

After the War
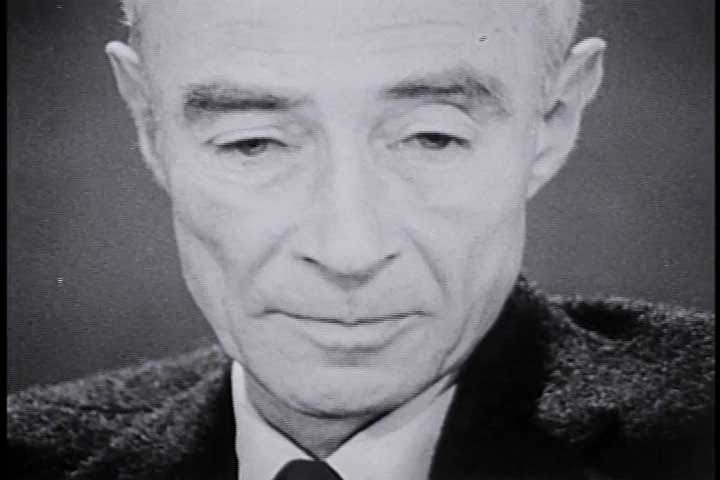
In the ensuing years, scientists continued to refine nuclear weaponry, leading to the development of the hydrogen bomb, with the Soviet Union also joining the fray. This sparked a global nuclear arms race that irrevocably altered international relations. Despite his pivotal role in the Manhattan Project, Oppenheimer opposed the use of nuclear arms and later advocated for nuclear non-proliferation. Reflecting on his contributions, he grappled with the realization that he had helped create a weapon capable of annihilating humanity, a burden he carried until his passing from throat cancer in 1967 at the age of 62.
The Oppenheimer Film
On July 21, the biographical film "Oppenheimer," directed by Christopher Nolan and featuring Cillian Murphy in the titular role, premiered. The film chronicles Oppenheimer's life and the repercussions of his work on the Manhattan Project, portraying the ethical dilemmas he faced during this tumultuous period. This article aims to provide context for those interested in viewing the film, though it only scratches the surface of Oppenheimer's complex life, including his fraught relationship with fellow scientist Heisenberg, who became a rival during the race to develop the atomic bomb.
Thank you for reading!
This video titled "Oppenheimer: The Father of the Atomic Bomb" delves into the life and legacy of J. Robert Oppenheimer, exploring his pivotal role in the development of nuclear weapons and the ethical implications of his work.
In this video, "OPPENHEIMER: The Decision to Drop the Bomb (1965)," experts discuss the moral considerations and political decisions surrounding the use of atomic bombs during World War II.