Exploring the Limitations of NLP Models in Math Word Problems
Written on
Chapter 1: Introduction to Math Word Problems
Consider this math word problem: “Yoshua recently turned 57. He is three years younger than Yann. How old is Yann?” This type of problem necessitates a comprehension of the narrative and logical reasoning to arrive at the correct answer. While a child might easily solve this, recent advancements in natural language processing (NLP) have shown that models can also achieve notable accuracy on similar tasks.
A recent investigation by a team from Microsoft Research has shed light on the methodologies employed by these NLP models, revealing some unexpected findings. Their research offers “concrete evidence” that many current solvers of math word problems (MWPs) primarily depend on superficial heuristics, raising doubts about their ability to consistently solve even straightforward problems.
Section 1.1: The Challenge of Math Word Problems
Math word problems are often complex, requiring machines to pull relevant details from textual descriptions and execute mathematical operations or reasoning to derive a solution. These problems vary significantly, with the simplest ones typically featuring a single unknown and basic arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division).
Subsection 1.1.1: Examples of Simple Math Word Problems

Researchers have started to apply machine learning techniques to more intricate MWPs, including those with multiple unknowns or those that involve concepts from geometry and probability. This line of research assumes that machines should easily solve basic one-unknown arithmetic problems. However, the paper titled Are NLP Models Really Able to Solve Simple Math Word Problems? challenges this assumption and introduces a new dataset aimed at evaluating these models more stringently.
Section 1.2: Key Contributions of the Research
The authors of the paper outline their main contributions as follows:
- Demonstrating that many problems in existing benchmark datasets can be solved using shallow heuristics that ignore word order or the actual question text.
- Introducing a challenge set named SVAMP, designed for a more rigorous assessment of methods aimed at solving elementary-level math word problems.
Chapter 2: Evaluating State-of-the-Art MWP Solvers
To underscore the limitations of state-of-the-art (SOTA) MWP solvers, the researchers conducted a series of experiments. They utilized two benchmark datasets: MAWPS and ASDiv-A, and evaluated three specific models: Seq2Seq, which employs a bidirectional LSTM Encoder and an LSTM decoder with attention; GTS, which features an LSTM encoder and a tree-based decoder; and Graph2Tree, which integrates a graph-based encoder with a tree-based decoder. In one set of tests, the team removed the questions, so the problems consisted solely of the narrative text.
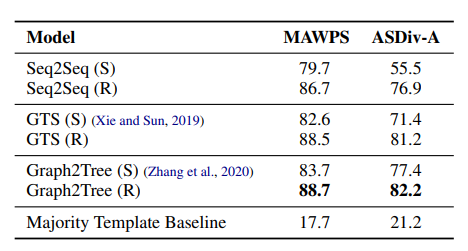
The findings indicated that Graph2Tree with RoBERTa pre-trained embeddings achieved the highest accuracy, recording 88.7% on MAWPS and 82.2% on ASDiv-A. Remarkably, even without the questions, Graph2Tree maintained strong performance, achieving 64.4% on ASDiv-A and 77.7% on MAWPS. These results imply that the models could derive answers without referencing the questions, suggesting a reliance on simple heuristics embedded in the problem narratives.
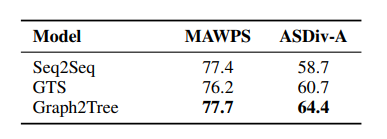
The researchers also experimented with a constrained model based on the Seq2Seq architecture, substituting the LSTM encoder with a feed-forward network. This model, utilizing non-contextual RoBERTa embeddings, achieved an accuracy of 51.2% on ASDiv-A and an impressive 77.9% on MAWPS, indicating that merely connecting specific words in the MWPs to their respective equations allowed the model to attain a high score.
Section 2.1: Introducing the SVAMP Challenge Dataset
In response to the identified shortcomings of SOTA MLP solvers, the researchers developed the SVAMP (Simple Variations on Arithmetic Math word Problems) challenge dataset. This new dataset comprises one-unknown arithmetic word problems modeled after those typically encountered in fourth-grade mathematics or lower. The researchers assessed the relative performance by training a model on one dataset and validating it on another.
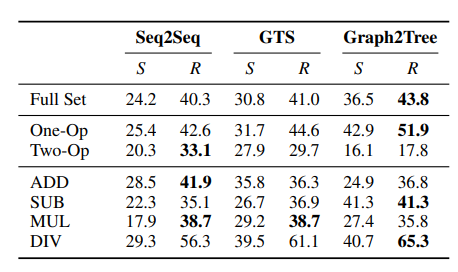
The findings indicated that the MWPs in the SVAMP dataset were less likely to be solvable through basic heuristics. Furthermore, even with additional training data, current SOTA models fell significantly short of performance expectations derived from previous benchmark datasets.
In conclusion, this research highlights concerning overestimations regarding the capabilities of NLP models in solving straightforward one-unknown arithmetic word problems, emphasizing that the development of robust methodologies for tackling even elementary MWPs remains a significant challenge.
The paper Are NLP Models Really Able to Solve Simple Math Word Problems? is available on arXiv.
Author: Hecate He | Editor: Michael Sarazen
