Understanding the Ease of Slipping Back into Unhealthy Habits
Written on
Chapter 1: The Nature of Bad Habits
It's often said that we won't truly break free from our bad habits until we genuinely despise the consequences they bring.

The remarkable evolution of human consciousness allows us to interpret our surroundings and our emotions. However, comprehending our own feelings and their influence on our actions remains a significant challenge. Throughout history, philosophers and stoics have documented principles for living a balanced life, drawing from their observations of human behavior and the nature of habits.
As Aristotle famously noted, "We are what we repeatedly do. Excellence, then, is not an act but a habit." This suggests that habits—whether positive or negative—can become automatic over time. The chemical and electrical signals in our brains, triggered by our emotions, play a crucial role in this process.
For instance, the joy we experience from happiness is linked to dopamine release, creating a sense of pleasure. Conversely, substances like alcohol can trigger a different chemical response, dulling our senses and impairing our cognitive functions. Moreover, drugs can lead to euphoric sensations that foster addiction, compelling individuals to seek out that same high repeatedly, which in turn heightens tolerance and addiction risk.
These patterns explain why individuals dealing with substance use disorders often find themselves escalating their drug use. The more I delve into this subject, the more I appreciate the complexity of our body's biochemistry and our ability to manage these responses.
So, why is it so easy to revert to harmful habits? They often provide immediate gratification.
Reflecting on my struggle with alcoholism, I recall how it nearly led to my downfall. Despite being acutely aware of its detrimental effects on my mental and physical health, the allure of alcohol was too powerful. In those moments, the temporary pleasure it provided overshadowed its destructive impact on my life. Overcoming such harmful temptations requires immense determination.
Pleasure is inherently enjoyable for both the mind and body, which explains our tendency to relapse into old habits. This leads us to a more focused question: how can we gain control over our carnal desires and addictive behaviors?
The Habit Loop
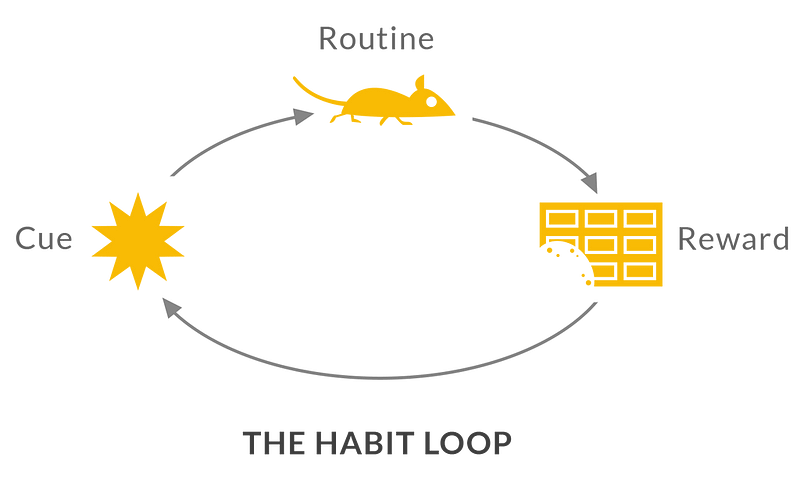
As described in Charles Duhigg's "The Power of Habit," the cycle of cue, routine, and reward becomes increasingly automatic over time. The anticipation and craving associated with habits can become deeply ingrained, leading us to believe that our habits define our destiny.
However, it's essential to remember that habits are not unchangeable. They can be ignored, altered, or replaced. Recognizing the habit loop is vital, as it reveals that when a habit forms, our brains often cease to engage in active decision-making. Unless we consciously confront these patterns, they will unfold automatically unless we establish new routines.
In my own journey to overcome alcoholism, I found success by employing this principle: I focused on ignoring any thoughts related to drinking until it became second nature to concentrate on more beneficial pursuits.
To effectively combat bad habits, we must consciously shift our focus from the reward that entices us to engage in these negative behaviors. It's crucial to replace that tempting "carrot" with something far more appealing.
While it may seem absurd to assert that bad habits can be challenging to eradicate, they are certainly not impossible to overlook. I hope you find the motivation to eliminate detrimental habits from your life, recognizing that they are choices we make rather than inescapable fates.
Thank you for taking the time to read this.
(I have no affiliations with any links mentioned in this article)
If you find value in my articles, consider supporting my writing by…
SUBSCRIBING to “FINDING NEW LIFE” by Carlos Jeronimo
Explore an archive of articles like this at carlosjeronimo.com
And if you wish to provide further support for my work…
Chapter 2: Insights from Neuroscience
This video features a neuroscientist explaining why breaking bad habits can be particularly challenging. It delves into the brain's chemistry and the psychological aspects that contribute to the persistence of unhealthy behaviors.
In this video, Mel Robbins offers practical advice on how to avoid falling back into old habits. She emphasizes actionable strategies for replacing negative patterns with positive ones.